Dog Oral Health and Care
The good news is that cavities are rare in dogs. The really bad news is that more than 80 percent of dogs over the age of three have gum disease, and among dogs adopted from shelters and rescue groups the percentage is closer to one hundred.
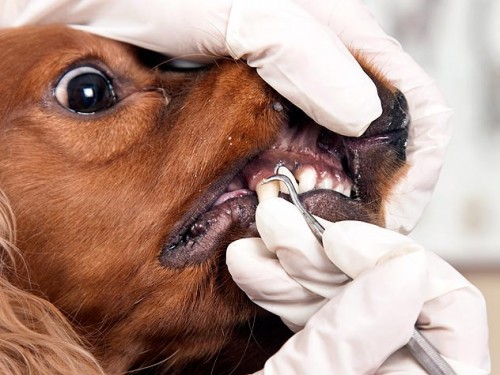
If he has other problems that need attention, they could be addressed at the same time. Although relatively expensive, regular professional dental care will make your dog feel better and keep his breath more pleasant for you to be near. Most important, good dental hygiene may prolong your dog’s life, because infected gums release bacteria into the bloodstream that can attack organs throughout the body.
Teeth cleaning is done under general anesthesia to give your vet free access to your dog’s mouth. Your vet, or her assistant, will remove tartar and plaque, and then polish your dog’s teeth. She will check for loose or damaged teeth, which may need to be removed or repaired, and for other signs of trouble. Different dogs need their teeth cleaned with varying frequencies, so be sure to talk to your vet about this.
There’s more to doggy dental care than vet visits. Between professional cleanings, bacteria cluster along your dog’s gum line. The bacteria form plaque, which hardens into tartar (calculus) if it’s not removed.
Tartar irritates the gums, causing gingivitis and periodontal (gum) disease characterized by abscesses, infections, and tooth and bone loss. To prevent or slow this destructive process, you need to brush your dog’s teeth.
Ideally, you should brush them every day, but every two or three days will go a long way toward preventing gum disease. Use toothpaste made for dogs — toothpaste for people can make your dog sick if he swallows it — and apply it with a brush designed for dogs, or a finger brush, or a small disposable dental sponge, whichever you find easiest.
Keep an eye out for signs of oral problems, including red, puffy gums; sudden or prolonged and copious drooling; swelling or lumps; ulcers and sores on the lips, gums, tongue, or other oral tissues; tenderness around the mouth; damaged teeth or tissues; inability to eat, or obvious discomfort when doing so; and foul breath. The sooner you catch a problem and bring it to your vet’s attention, the better for your dog and, probably, your wallet.
In addition to a good dental care regimen, you can help keep your dog’s mouth and teeth healthy by feeding him high-quality food, and by providing him with safe chew toys that help clean his teeth and gums.
The more you can do to remove plaque and tartar from your dog’s teeth between veterinary visits, the less frequently your dog will need to undergo a veterinary dental treatment. Since the procedure involves anesthesia — which is never without some risk — and can be costly, it’s in your and your dog’s best interests to follow a regular dental health regime at home.





